Table of Contents
THREAT HUNTING 101
A Comprehensive eGuide
What is threat hunting?
Advanced threat actors slip past the initial
security defenses set up by organizations.
These malicious attack vectors can remain in
the network for months trying to move
laterally across the environment with the help of confidential data or login credentials.
Threat hunting is a process usually followed
by Security Analysts to search for such
anomalies in an organization’s environment to
identify cyber threats that may be lurking undetected in a network. This approach is an
essential component of a robust cyber
defense strategy and combines a proactive
methodology, innovative technology, and
threat intelligence to stop attacks before
they successfully penetrate an organization’s
defenses.

Why threat hunting?
The third quarter of 2022 witnessed a 70% increase in breaches compared to the previous quarter. The rapid and alarming rate of increase in cyber-attacks is only expected to accelerate further in 2023. The increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks leaves no room for doubt – it is important now, more than ever, for organizations to stay one step ahead of cyber threats and respond to them proactively. Organizations will need an arsenal of tools that include antivirus, firewalls and SIEM platforms along with new and emerging technology to hunt adversaries, detect anomalies and identify vulnerabilities in their network environment.
A proactive threat hunting approach enables threat hunters to become familiar with the organization’s environment, network, and architecture to filter out and closely monitor key events by leveraging both emerging technologies and human skills. It also helps identify the potential target of the attacks as well as their patterns and the steps followed at a very initial stage. Threat hunting reduces the time taken to detect an anomaly after the occurrence of an incident, thereby minimizing its impact on core systems, thus facilitating quick patches to vulnerabilities. With the right tools, techniques and training, threat hunters can formulate a hypothesis around a malware, threat group or any other possible attack vector to determine whether it is present in the organization’s environment. Threat hunters can then leverage the hypothesis generated from various sources like zero-day vulnerabilities, threat intelligence or incident reports, as a starting point for further investigation.
Proactive threat hunting is a critical component of a robust cyber defense strategy and enables organizations to stay one step ahead of the ever evolving and rising sophistication of cyber-attacks.
Types of threat hunting
When threat hunters start to search for unknown threats present in an organization’s environment, they first investigate all the events to detect suspicious activities or system vulnerabilities that can disrupt our put the environment as risk. Threat hunting investigations are classified into three key categories:

Structured threat hunts are built around a central hypothesis relating to specific threat actors, their tactics, techniques, procedures (TTPs) and attack patterns. This enables threat hunters to identify a threat actor before it can damage the targeted systems.
Unstructured hunting is based on the
logs or the alerts that are triggered by
monitoring tools. Triggered alerts such
as indicators of compromise (IOC),
blacklisted IPs, or unknown executables
work as a cue for threat hunters to
further dig and analyze older as well as
upcoming logs and take necessary
action to mitigate the risk.
Situational investigation is based on the
hypothesis unique to an enterprise that
is developed from an organization’s
internal risk assessment, vulnerability
analysis or latest threat intelligence.
Threat hunters reference this internal
and crowdsource data to search
cyberattack trends and reveal the latest
TTPs of a potential threat.
Threat hunting tools
The process of threat hunting is usually built on the foundation of planning, baselining, and testing based on the hypothesis formulated by experienced cybersecurity professionals. Besides these, a threat hunter can also use automated tools or platforms to boost threat analysis and identify any suspicious patterns and relationships on a large scale. These tools help them investigate existing logs and ensure that relevant alerts are triggered when a suspicious event occurs.

Some of these tools are:
A combination of security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM), SIEM solutions provide real-time analysis of security threats and offer tracking and logging of security data. It helps threat hunters to conduct an in-depth investigation of any anomalies and irregularities to find the root cause of an incident and take swift action. Recognized as a staple in modern-day security operations centers (SOC), SIEM has evolved to automate many manual processes associated with threat detection and incident response with the use of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Some of the prominent SIEM tools available in the market are Splunk, IBM Qradar, ArcSight, LogRhythm, and SolarWinds.
MDR is a cybersecurity platform that remotely
monitors, detects, and responds to threats.
By combining both human expertise and
technology, MDR helps organizations identify
threats and limit their impact. It offers analysts
with threat intelligence, advanced analytics,
and forensic data to detect anomalies, respond to alerts and restore the affected endpoint to its normal state. MDR enables
threat hunters to identify and alert on the
threats that might have been missed by the
automated layers of security defenses.
Getting the Basics Right
Threat hunting is not just the use of SIEM and MDR tools but is the effective monitoring and management of log data across an organization’s computer systems, servers, and networks.
A combination of security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM), SIEM solutions provide real-time analysis of security threats and offer tracking and logging of security data. It helps threat hunters to conduct an in-depth investigation of any anomalies and irregularities to find the root cause of an incident and take swift action. Recognized as a staple in modern-day security operations centers (SOC), SIEM has evolved to automate many manual processes associated with threat detection and incident response with the use of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Some of the prominent SIEM tools available in the market are Splunk, IBM Qradar, ArcSight, LogRhythm, and SolarWinds.
They inspect network packets, block
suspicious ones, and notify administrators
of attempted attacks. The logs of these
systems contain valuable network threat
information about attack types, targeted
devices, and malicious traffic sources.
It manages and secures communication between browsers and the websites and
services they access. It entails regularly checking DNS records for any unexpected
changes or localized outages in order to detect potential security breaches.
It primarily employs signature-based detections to identify threats on a system,
which aids in the tracking of common malware and hacking tools. It also aids in the identification of notable threats and provides insight into trends and coverage
from antivirus solutions.
Organizations generate massive amounts of log data and events through applications, networks, systems, and users, and therefore require a systematic process to manage and monitor disparate data across log files. The combination of network-level security logs, authentication logs and application-level audit logs help provide complete visibility of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Logs generated from Firewalls, Intrusion Detection System (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), Domain Name System (DNS) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Antivirus etc., are a crucial component of forensics, compliance, and real time threat hunting. These log sources provide a detailed record of every action and thus provide insights to help identify the root cause of problems or anomalies. Correlation rules and AI/ML tools work much better in tandem with these logs as well.
Analyzing an attack
Threat hunting is a proactive and challenging process, and it is not easy to document rapidly evolving adversarial techniques. Understanding how attacks work is critical to devising defense strategies and for that hunters need to use detailed threat intelligence relating to the anatomy of an attack. Highlighted below are some of the threat intel frameworks that are useful for a threat hunter to analyze the movement and minimize the impact of a threat actor.

Organizations generate massive amounts of log data and events through applications, networks, systems, and users, and therefore require a systematic process to manage and monitor disparate data across log files. The combination of network-level security logs, authentication logs and application-level audit logs help provide complete visibility of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Logs generated from Firewalls, Intrusion Detection System (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), Domain Name System (DNS) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Antivirus etc., are a crucial component of forensics, compliance, and real time threat hunting. These log sources provide a detailed record of every action and thus provide insights to help identify the root cause of problems or anomalies. Correlation rules and AI/ML tools work much better in tandem with these logs as well.
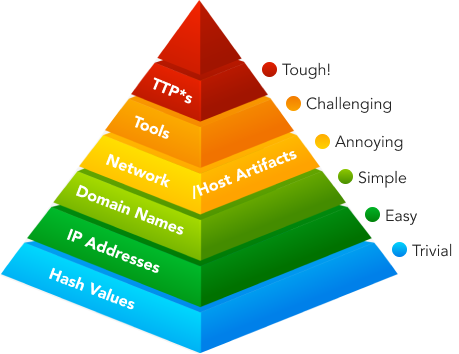
Pyramid of Pain
In 2013, David J Bianco came up with the concept of Pyramid of Pain that represents six types of attack indicators that the analyst must look out for, to detect the activities of an adversary. The indicators arranged in ascending order represent the amount of pain an adversary needs, to adapt to, pivot and continue with the attack even when the indicators at each level are being denied. A threat hunter can employ the different types of indicators of compromise (IOC) illustrated at each level to detect an attacker’s activities. While identifying and preventing the IOCs at each level, the hash values, IP addresses and domain names can be accessed through commercial threat intelligence feeds; network and host artefacts can be accessed via micro threat intelligence feeds; robust security programs are necessary to detect and prevent threat actor’s tools and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
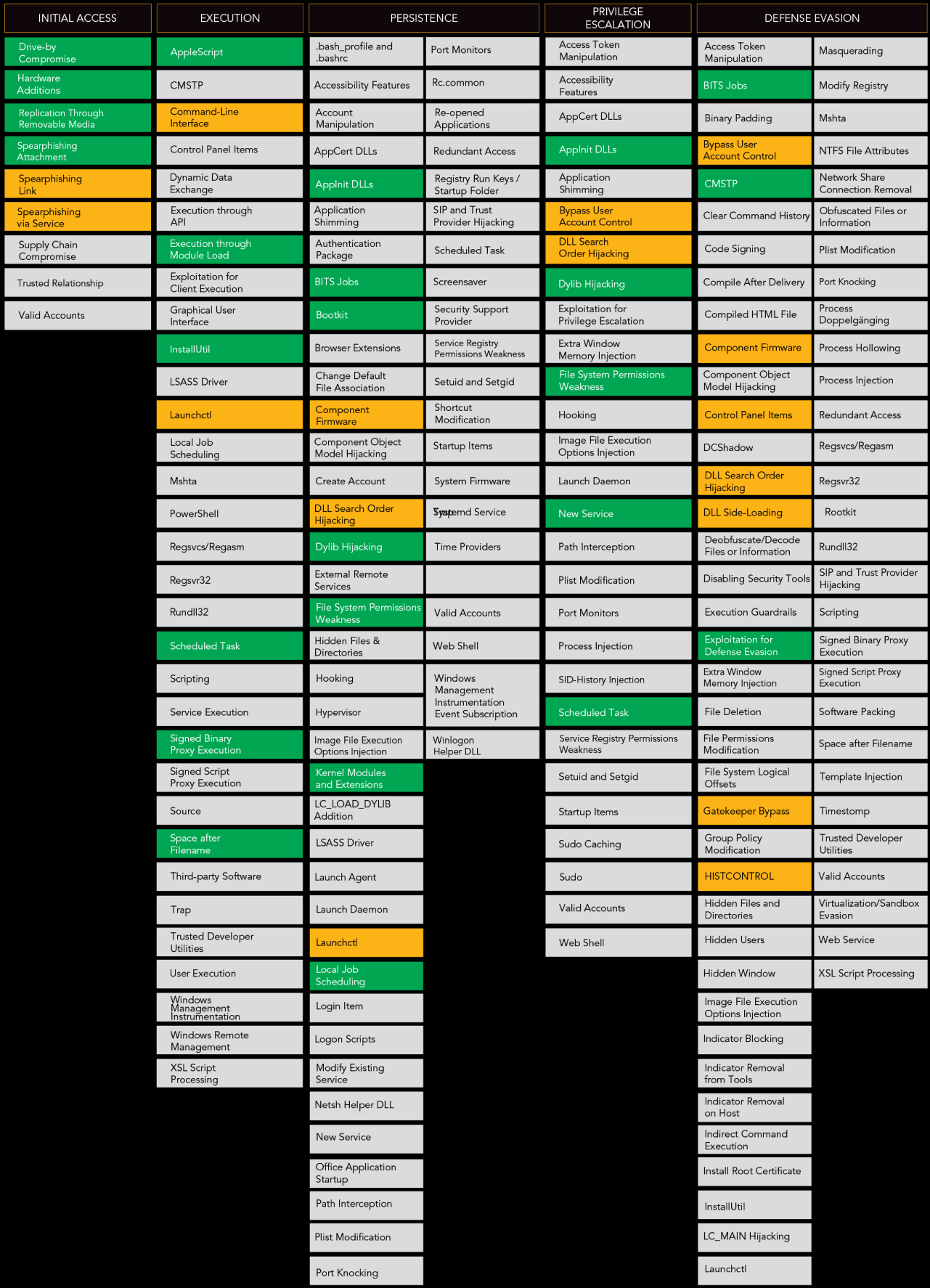
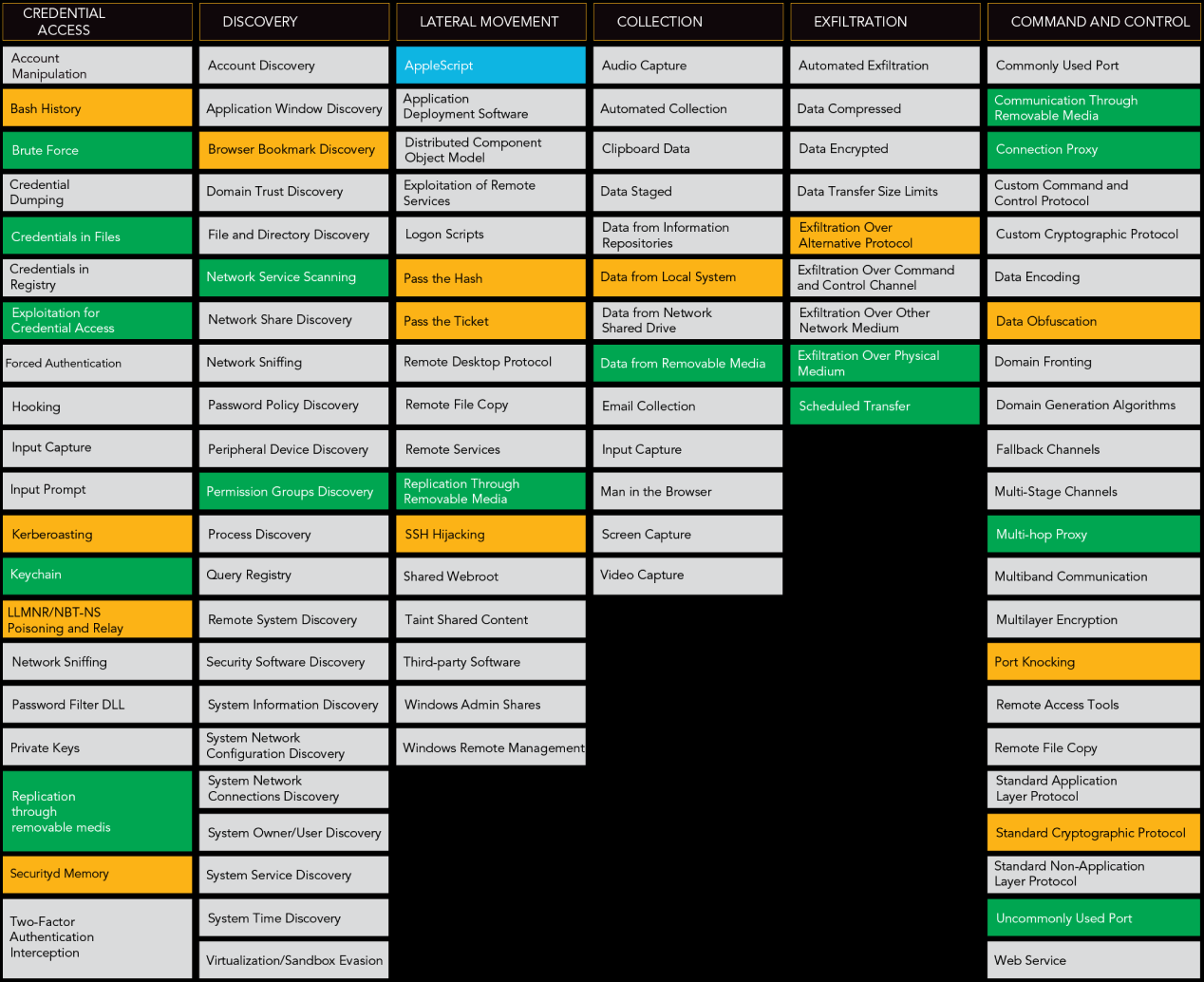
MITRE ATT&CK Framework
MITRE’s Adversarial Tactics, Techniques and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK) is a threat intelligence resource and a knowledge base of attacker’s TTP based on real world observations. The framework lists 11 tactics and multitude of techniques used by threat actors to compromise any network. Threat hunters can leverage this model to build contextual threat models and determine the tools and techniques an attacker can use for a successful attack on their organization. It helps hunters broaden their scope of hypothesis, understand attacker’s profile and behavior, gather data, and investigate the potential targets of any attack. Each step of the investigation from initial access and execution to exfiltration and command & control, hunters can feed indicators of compromise and indicators of attack that are relevant to the context of their organization. This helps improve the organization’s monitoring and detection capabilities and elevates the overall security posture.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework helps threat hunters build contextual threat models and determine the tools and techniques that an attacker can use for a successful attack.
Threat hunting techniques
Threat hunting is a human-driven and systematic process that helps reduce breaches, increase speed and accuracy of incident response, and improve security defenses. But there is more than just one way to hunt for threats and fight against adversaries. A few of the most common threat hunting techniques that security teams can use to identify the threats are listed below.

A reactive hunting strategy, intel-based hunting is a technique based on input sources of intelligence such as IOCs, IP addresses, hash values and domain names, networks, or host artifacts. These predefined rules can be integrated with SIEM and other threat intelligence tools to observe and inspect the networks and systems. To identify any compromise in the environment, intelligence sharing platforms such as computer emergency response teams (CERT) can also be used to export automated alerts and input into the threat hunting tools as structured threat information expression (STIX) or trusted automated exchange of intelligence information (TAXII).
To identify malware attacks and persistent
threat groups, hypothesis-based threat
hunting technique leverages MITRE ATT&CK
framework and threat hunting library. Using
this proactive approach, threat hunters can
identify the threat actors by using IOAs and
TTPs, assess its attack behavior to create
hypothesis, and monitor the environment to
timely detect the anomalies.
Custom hunting technique is based on situations and can be a combination of both intel-based and hypothesis-based threat hunting. It is customizable based on the
requirements and involves using situational
awareness and existing information about the
environment.
Threat hunting methodology
An effective threat hunting exercise is an iterative combination of processes, tools and techniques that align with the organization’s structure. While there are some basic steps and processes that one can follow for an efficient hunting program, threat hunters still need to think out of the box and expand their scope of investigation to ultimately outwit the attackers.

Just having raw data is not enough to conduct a meaningful hunt. Hunters must
use tools that provide a detailed picture of data like network traffic patterns, file
hashes, system and event logs, user activity, file operations and all other activities.
Detecting abnormal activities triggered by threat actors becomes easier if threat
hunters understand the baseline normal. Determining the organization’s
structure, its framework , business activities and user behaviors helps create
hypothesis to investigate anomalies.
Hypothesis formation and testing includes leveraging tools, frameworks, threat
intel and past experiences to quickly detect the root cause behind the threats
and efficiently respond to them. Some of the widely used threat intelligence
include Virus total, IBMM Xforce, and AlianVault.
The next step involves discovering malicious patterns in the data cycle and
uncovering the attacker’s TTPs with the help of various tools and techniques.
It helps validate the nature, impact, and scope of the generated hypothesis.
After uncovering any anomaly, it is essential to neutralize the threat with rapid response and remediation. In addition to protecting the system from a perceived threat, hunters must initiate measures that help prevent similar attacks in the future as well.
The last step includes using the discoveries made during an investigation to form a basis for automated analytics. This improves EDR systems and helps
analyze future incidents more effectively, compared to the knowledge base
generated.
Challenges of threat hunting
Threat hunting is a time-consuming affair and requires around the clock monitoring along with cybersecurity expertise. In addition to being a time-consuming effort, lack of adequate budgets also restricts organizations from having an effective threat hunting platform.

Cyber threat hunting requires expert threat hunters capable of identifying the indicators of sophisticated attacks at a very early stage to prevent an organization from getting breached. As cybersecurity skills gap widens impacting over 57% of organizationsII worldwide, deploying the right workforce for the exercise becomes a part of the challenge.
Access to both current and historical data is a key component of initiating a hunt. Missing any crucial information can lead to lack of informed hypothesis based on network, endpoints, or
cloud infrastructure.
Threat hunters must stay abreast with threat intelligence to analyze IOCs and protect their organization’s network, data,
users and reputation from evolving adversaries. Additionally, the platform used must be capable of integrating the latest
intelligence to develop meaningful attack hypothesis. With outdated knowledge, analyzing potential network threats can become a challenging task.
Future of threat hunting
Industries across the globe are caught up in a whirlwind of massive technological innovation on the one hand and exponential growth of data on the other. As the attack surface widens at a rapid pace, it is likely to open multiple gateways for threat actors to breach networks and exploit unpatched vulnerabilities. Over the years, this high-speed evolution has prompted organizations to use proactive solutions like threat hunting due to its proven effectiveness. This trend is likely to continue in the coming years.
However, as we progress forward, relying only on terabytes of threat intel information and manual analysis of anomalies could prove to be exhausting for threat hunters. Moreover, emerging sophisticated attack vectors that are familiar with widely used simplistic rules and analytics, may also render most threat hunting programs less effective. It is crucial for organizations to equip threat hunting teams with advanced tools that leverage AI and ML algorithms to identify anomalies, and outwit evolving attack techniques used by hackers.
Proactive solutions like threat hunting have proven their effectiveness amidst an exponential increase in the attack surface. The uptick in adoption is expected to continue in the coming years.
SISA ProACT and threat hunting
SISA ProAct, a Forensics-driven MDR solution is an end-to-end platform combining intuitive security analytics dashboards, scalable virtual appliances, and a proprietary all-in-one agent. It provides an integrated monitoring platform and a unified incident response solution to help organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture. SISA ProACT, enabled by SISA’s in-house developed machine learning algorithm, provides a comprehensive approach to reduce the false positives and relieves enterprises from alert fatigue situations. A scalable solution that supports all platforms and deployment architectures including on-premises, cloud, co-location, and hybrid cloud deployments, SISA’s MDR solution facilitates faster integration with enterprise network components and scales rapidly to help enterprises accelerate time to value.
References
- https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/data-breaches-rise-by-70-q3-2022/
- https://venturebeat.com/security/studies-show-cybersecurity-skills-gap-is-widening-as-the-cost-of-breaches-rises/
- https://attack.mitre.org/
- https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/capabilities/cyber/cyber-kill-chain.html
- https://www.sans.org/tools/the-pyramid-of-pain/
Table of Contents

SISA is a global forensics-driven cybersecurity solutions company, trusted by leading organizations for securing their businesses with robust preventive, detective, and corrective cybersecurity solutions. Our problem-first, human-centric approach helps businesses strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
Industry recognition by CREST, CERT-In and PCI SSC serves as a testament to our skill, knowledge, and competence.
We apply the power of forensic intelligence and advanced technology to offer true security to 2,000+ customers in 40+ countries.
Company
Resources
Quick Links
Copyright © 2024 SISA. All Rights Reserved.
 USA
USA India
India APAC
APAC Middle East
Middle East Global
Global
 Facebook
Facebook Linkedin
Linkedin  X
X Youtube
Youtube







